5 Ways To Improve Pedestrian Safety For All Residents
August 14, 2023
By Gus Perron, Project Manager, WSB
In recent years, there has been a distressing increase in pedestrian-vehicle collisions, highlighting the vulnerability of pedestrians on the road. Several reasons have contributed to this surge including the unforeseen impact of COVID-19, which kept people off the roads for extended periods, leading to increased speeds and reduced vigilance. Moreover, distracted driving due to the prevalence of smartphones and electronic devices, impaired driving, speeding and inadequate pedestrian infrastructure have all played a role in pedestrian-related accidents and fatalities.
Combating this concerning trend necessitates a comprehensive approach encompassing awareness campaigns, responsible driving habits, and improved infrastructure to prioritize pedestrian safety and reduce these tragic accidents.
Here are five things communities can do to increase pedestrian safety.
Implement a Complete Streets policy
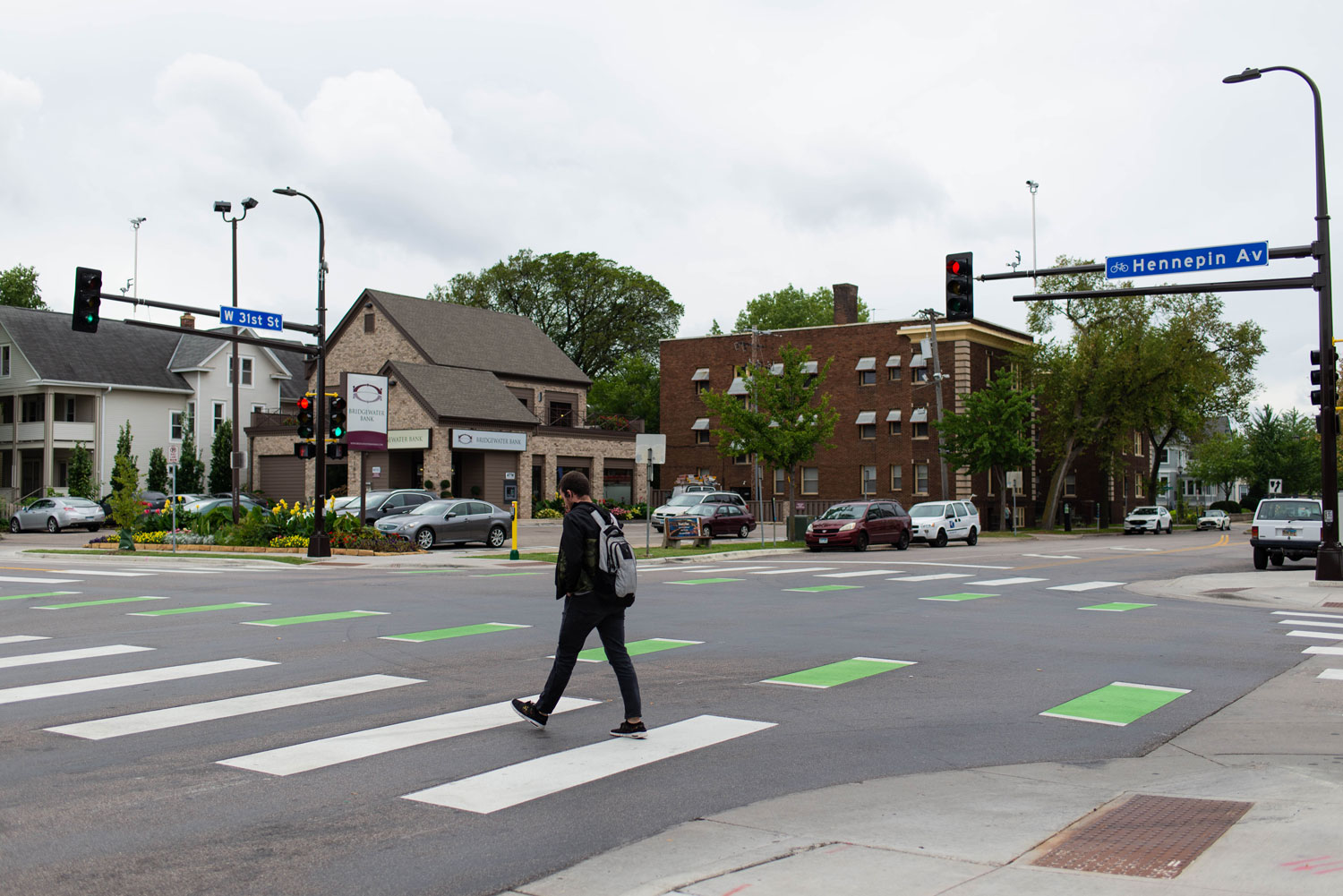
Communities should consider a Complete Streets transportation policy that prioritizes the safety and accessibility of all road users. That means finding balance and designing streets that cater to pedestrians, cyclists, public transit users and motorists. Complete streets encourage active transportation and promote pedestrian safety. With dedicated bike lanes, well-marked crosswalks and improved transit facilities, the policy fosters a pedestrian-friendly environment while enhancing overall traffic flow. By combining these elements and striking a balance, communities can advance holistic solutions to improve safety for all users.
Protect students with Safe Routes To School
Safe Routes to School is a national program dedicated to enhancing pedestrian safety for students traveling to and from school. By funding and implementing infrastructure improvements and traffic calming measures, Safe Routes to School creates safer pathways, crosswalks and bike lanes for children. Moreover, the program emphasizes educational initiatives to promote road safety awareness and responsible pedestrian behavior. Cities should explore grant funding opportunities for safe routes to school projects.
Adopt a policy on uncontrolled crossings
Uncontrolled crossings, characterized by the absence of stop signs or traffic signals, pose significant safety challenges for pedestrians. To address this issue, it is crucial to develop a comprehensive policy that clearly communicates what a community’s rules and priorities are at these types of crossings. Building local support is essential in gaining traction for the implementation of appropriate measures which could include installing marked crosswalks, warning signs, pedestrian refuge islands, curb extensions (bumpouts) or beacons to enhance pedestrian visibility and safety. By proactively addressing uncontrolled crossings, local authorities can create safer road environments and protect pedestrians and drivers from potential hazards.
Design facilities for pedestrians of all abilities
Ensuring safe and accessible facilities for pedestrians with physical disabilities at crossings is of the utmost importance, a protected civil right. There must be sufficient signal crosswalk times so people with mobility issues can cross safely. Additionally, implementing detectable warning surfaces at curb ramps can serve as tactile indicators for those with vision impairments, alerting pedestrians that the protection of the sidewalk is ending and a crosswalk is beginning. Sidewalks should also be wide enough and without barriers, cracks, large gaps, etc. to ensure they are usable for people with disabilities including wheelchair users.
By incorporating these features, municipalities can enhance pedestrian safety and create a more inclusive and accommodating environment for everyone.
Consider the technology and tools that work best for a crossing
Different types of beacons can serve different types of crossings, so communities should explore what works best. RRFB (Rectangular Rapid Flashing Beacon) warning lights can be installed, requiring pedestrians to push a button to activate flashing lights, alerting vehicles that people are crossing. Alternatively, a Pedestrian Hybrid Beacon, activated by pedestrians, can operate similarly to a traffic light, flashing yellow and red to control traffic flow. Although the Pedestrian Hybrid Beacon may cost more upfront, it becomes more advantageous for pedestrians in areas with higher traffic volume or faster vehicle speeds. By integrating these technologies, communities can improve the overall pedestrian experience and improve safety.
How WSB can help
WSB plays a vital role in enhancing pedestrian safety and accessibility. We can help communities identify funding, develop policies, as well as scope, design, and construct pedestrian infrastructure enhancements. By thoroughly analyzing the impact of traffic solutions for vehicles and pedestrians, including those using mobility devices, they ensure comprehensive and inclusive planning, balancing the needs of pedestrians, bicyclists, and motorists. Drawing from their depth of experience, WSB actively listens to clients’ needs, tailoring individualized plans that address specific community needs. With a keen focus on safety, WSB considers existing speeds, crossing widths and traffic volumes to identify the most effective solutions to mitigate potential fatalities. Leveraging the latest technological tools for data collection, WSB can assess data to identify areas of highest need, allowing for practical and data-driven improvements.
Gus is WSB’s expert in accessible pedestrian and bicycle facilities, with a traffic engineering background which allows him to blend pedestrian accessibility with safety and mobility. He uses best practices to achieve constructable and usable pedestrian facilities for a variety of project scopes across different environments.
[email protected] | 612.360.1296