By Robert Slipka
Feb. 6, 2015
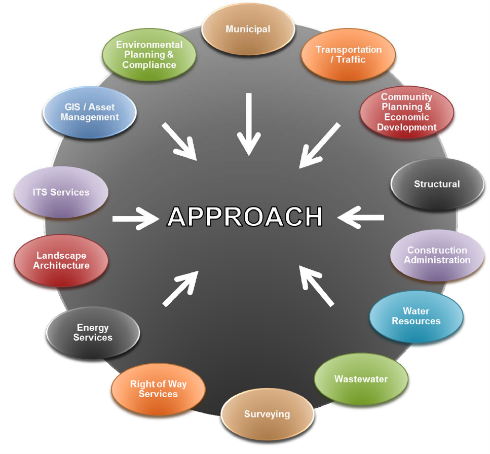
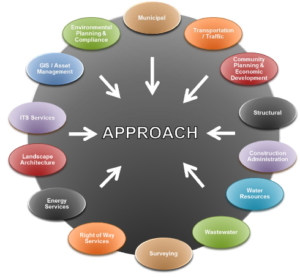
Integrated design brings together a diverse team of design professionals on one project. Projects benefit from this approach because a wider range of experts is contributing throughout the project as a team, rather than acting independently.
Early integration is crucial to reduce the potential for expensive conflicts as design progresses or implementation begins. The integrated design approach involves all parties, including design professionals, clients/owners, permitting agencies, and others. Involvement may also include cost analysis specialists, construction managers, and contractors.
No matter what that project type, an integrated approach helps ensure a holistic outcome rather than a culmination of interdependent elements. Below are two examples of what teams could look like.
Example 1
A site development project is led by a landscape architect or civil engineer with direct integration of specialists such as environmental scientists, ecological specialists, engineers, building architects, electrical engineers, irrigation designers, and the client (including their operations and maintenance staff).
Example 2
A roadway corridor project is led by a transportation engineer and/or a planner. The team for this type of project may integrate urban designers/landscape architects, engineers, environmental scientists, right-of-way specialists, and representatives from numerous government agencies.
Design charrettes and brainstorming sessions are often utilized heavily in the beginning phases of project planning and design. This helps the team identify key goals, strategies, and desired outcomes of the project while also establishing areas of conflict or design implications. Including a diverse range of professionals means a better likelihood of achieving creative solutions that might not be explored in a conventional, non-integrated approach. As the project develops into the construction documents phase, continued collaboration is required to ensure compatibility of spatial character, uses, spaces, materials, and other factors. This approach can also identify conflicts that might not otherwise be identified until late in design or into construction, avoiding unanticipated costs or redesign.
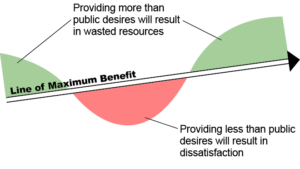
Although an integrated approach provides better results, it is important for consultants and clients to judge how extensively integration needs to occur based on costs and benefits. Some projects are smaller in scale or fee, which can make an elaborate integrated approach difficult to justify. Clients should also be aware that the term “one-stop shop,” often utilized to describe multi-disciplinary firms, does not necessarily mean that an integrated design approach is used for projects. If it is unclear or unproven, clients should ask the consultant to describe how the various team members will be integrated throughout the design process. The ultimate goal is to achieve higher quality projects with increased cost effectiveness to clients.